🔥 Rewriting History & Overcoming Git-asters
⚠️ Advanced Git: History Manipulation
Learn to rewrite history, understand rev-parse, and master git reset - the most powerful (and dangerous!) Git commands
🎯 Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you'll understand:
- How Git references work with
rev-parse - The three modes of
git reset(soft, mixed, hard) - When and why to rewrite history
- How to safely manipulate commits
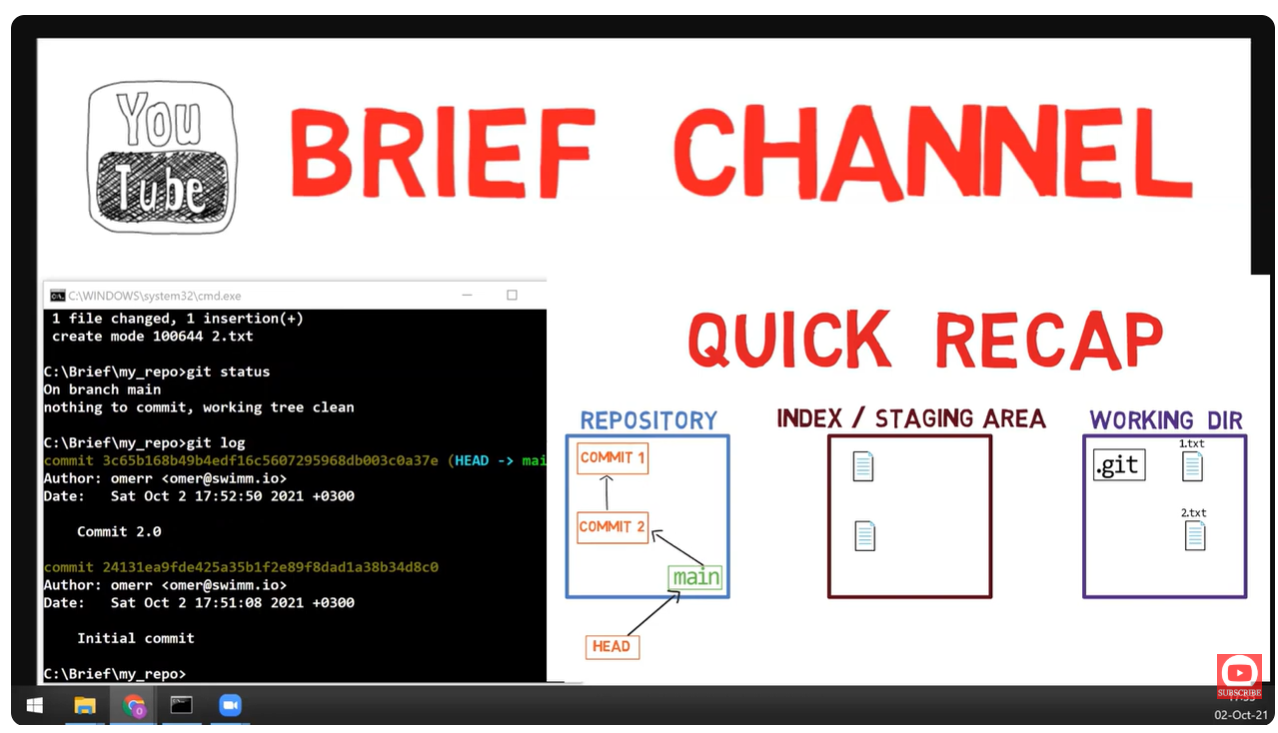
📜 Part 1: Understanding Git References
What is rev-parse?
git rev-parse is the Swiss Army knife for resolving Git references. It translates human-readable names into SHA-1 hashes.
Common Reference Patterns
# Get the current commit SHA
git rev-parse HEAD
# e.g., a1b2c3d4e5f6...
# Get the parent commit
git rev-parse HEAD~1
# or HEAD^
# Get 3 commits back
git rev-parse HEAD~3
# Get a branch's commit
git rev-parse main
git rev-parse feature-branch
# Get the tree of current commit
git rev-parse HEAD^{tree}Reference Syntax Cheat Sheet
| Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|
HEAD | Current commit |
HEAD~1 or HEAD^ | First parent |
HEAD~2 | Grandparent (2 commits back) |
HEAD~n | n commits back |
HEAD^2 | Second parent (for merges) |
HEAD^{tree} | Tree object of commit |
HEAD:path/to/file | Blob at path in commit |
@{-1} | Previous branch |
@{upstream} | Upstream tracking branch |
⚡ Part 2: The Problem - "Git-asters" Happen!
Common Git Disasters
"I just committed to main instead of feature!"
"Typo in commit message, already pushed!"
"Accidentally committed .env file!"
"5 WIP commits should be 1 clean commit"
🔧 Part 3: Master rev-parse First!
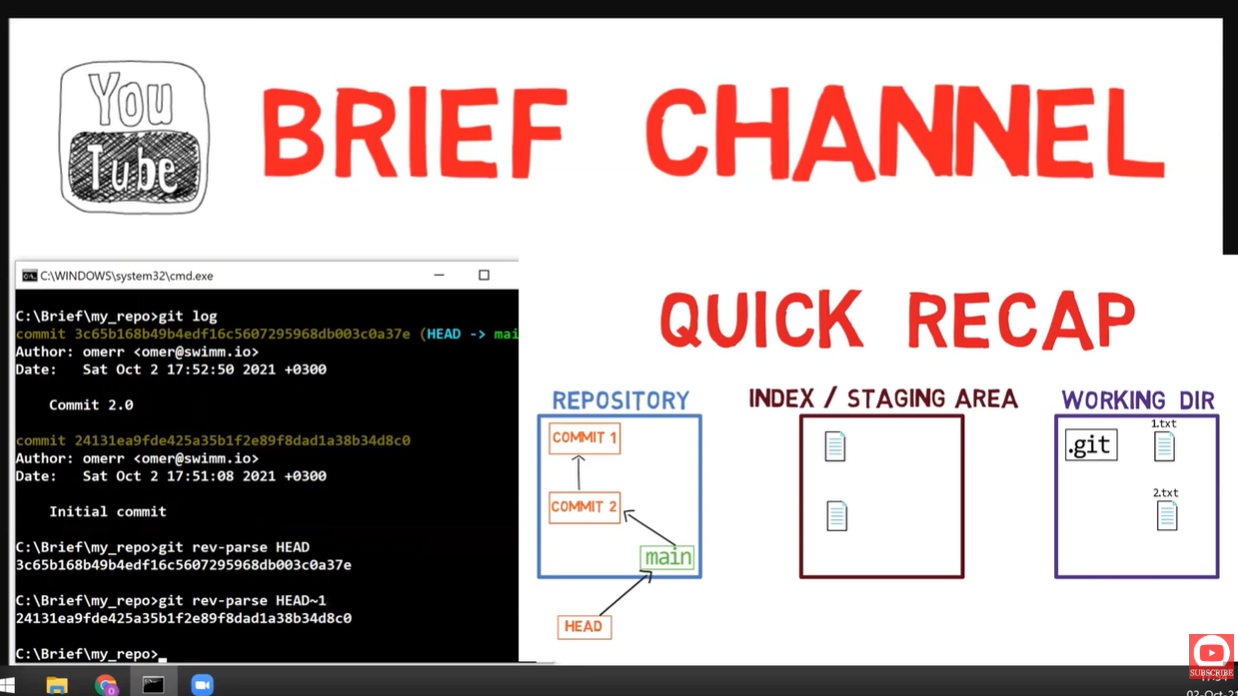
Why rev-parse Matters
Before you can rewrite history, you need to navigate it. rev-parse is how Git internally resolves references.
# Practical examples
git rev-parse HEAD # Current commit
git rev-parse --short HEAD # Short SHA (7 chars)
git rev-parse --verify HEAD # Verify it exists
# Find common ancestor
git merge-base main feature
# Show what HEAD points to
git symbolic-ref HEAD
# refs/heads/main🧪 Try It: Reference Resolution Lab
# Create a test repo
mkdir rev-parse-lab && cd rev-parse-lab
git init
# Create some commits
echo "v1" > file.txt && git add . && git commit -m "First"
echo "v2" > file.txt && git add . && git commit -m "Second"
echo "v3" > file.txt && git add . && git commit -m "Third"
# Now explore!
git rev-parse HEAD # Third commit
git rev-parse HEAD~1 # Second commit
git rev-parse HEAD~2 # First commit
# Verify they're different
git log --oneline🚀 Part 4: Git Reset - The Three Modes
⚠️ Warning: Reset Rewrites History!
git reset moves the branch pointer backward, effectively "undoing" commits. This is powerful but dangerous - especially if you've already pushed!
The Three Reset Modes Visualized
🟢 Reset Mode 1: --soft
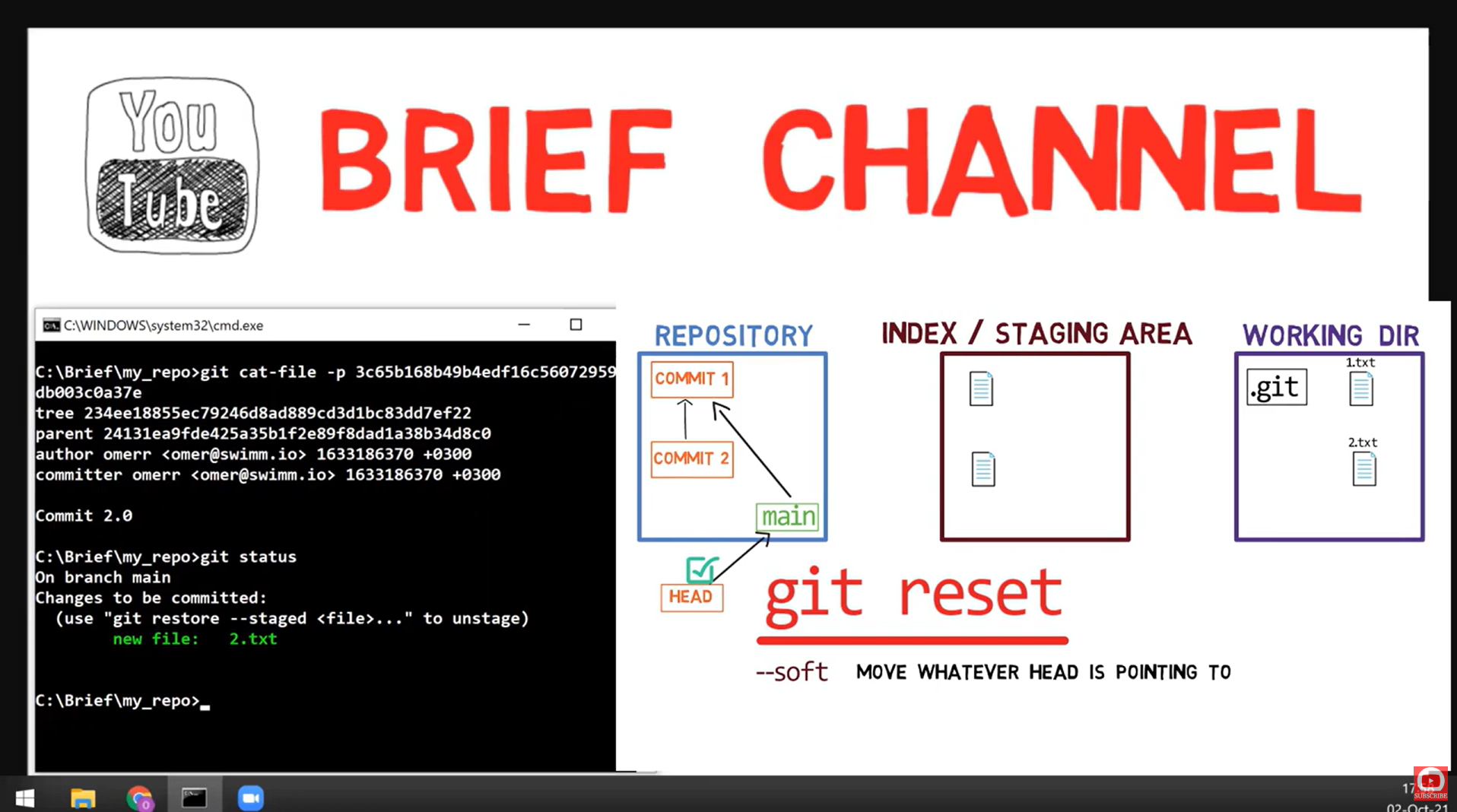
What --soft Does
- HEAD moves back
- Index (staging) stays the same
- Working directory stays the same
- Your changes are still staged, ready to recommit!
Perfect For: Squashing Commits! 🎯
# You have 5 messy commits
git log --oneline
# abc1234 WIP fix
# def5678 more fixes
# ghi9012 oops typo
# jkl3456 feature work
# mno7890 started feature
# Soft reset to BEFORE all 5 commits
git reset --soft HEAD~5
# All changes are now staged!
git status
# (shows all changes ready to commit)
# Make ONE clean commit
git commit -m "feat: complete feature implementation"
# 5 commits → 1 commit! 🎉"I am powerful with git reset now muhahaha! I got an idea - I don't need rebase, I can just squash things pretty easily!"
🟡 Reset Mode 2: --mixed (Default)

What --mixed Does
- HEAD moves back
- Index resets to match new HEAD
- Working directory unchanged
- Your changes are there but UNSTAGED
Perfect For: Reorganizing Commits
# Committed too much in one commit?
git reset HEAD~1
# Files are still there, but unstaged
git status
# Changes not staged for commit:
# modified: file1.js
# modified: file2.js
# modified: file3.js
# Now stage them selectively
git add file1.js
git commit -m "feat: add feature 1"
git add file2.js file3.js
git commit -m "fix: bug fixes"
# 1 big commit → 2 focused commits!🔴 Reset Mode 3: --hard
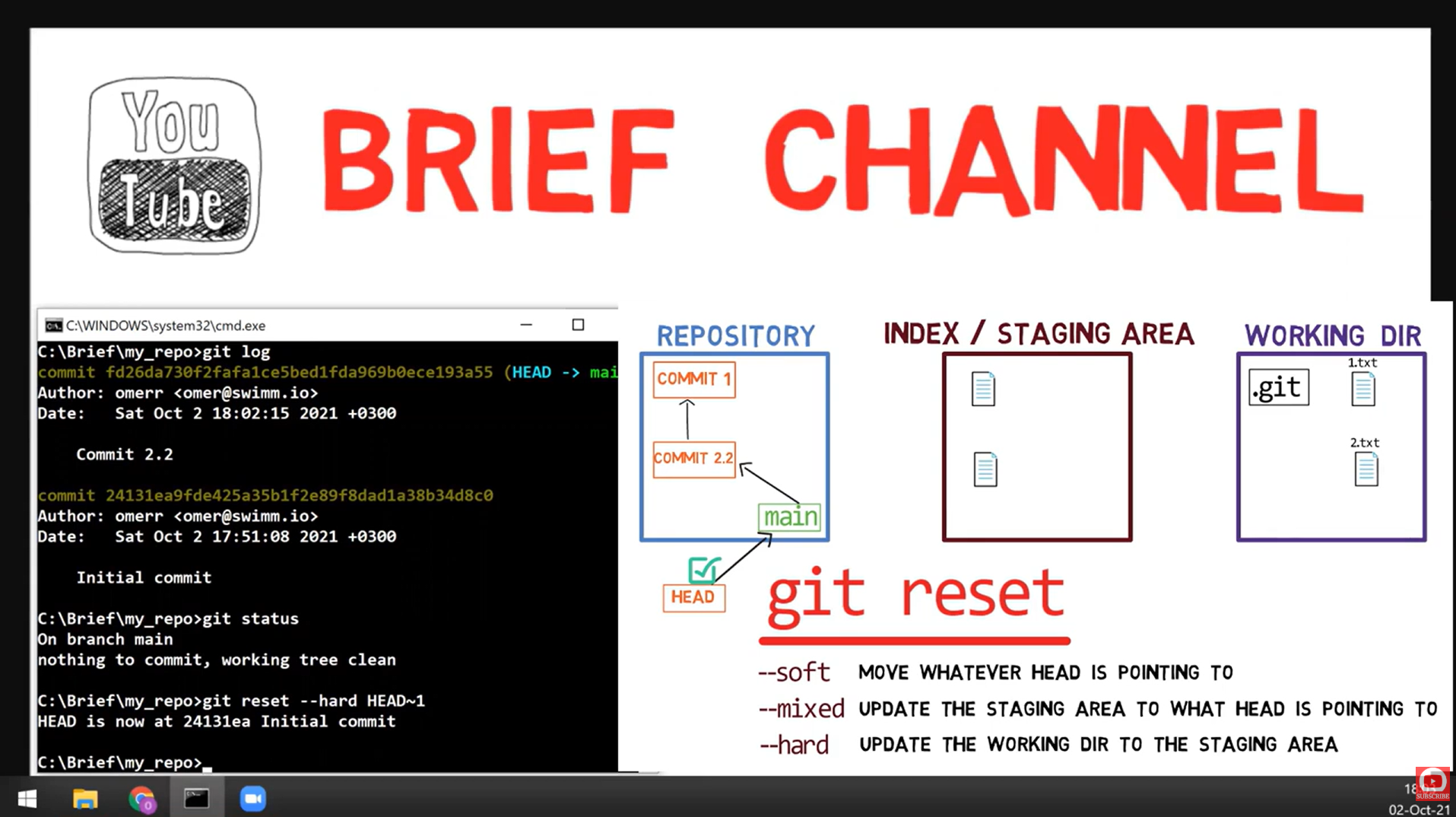
What --hard Does
- HEAD moves back
- Index resets completely
- Working directory WIPED to match HEAD
- ⚠️ UNCOMMITTED CHANGES ARE LOST FOREVER!
Use With EXTREME Caution!
# Completely throw away last commit AND all changes
git reset --hard HEAD~1
# ⚠️ No going back (unless you know reflog!)
# Discard all uncommitted changes
git reset --hard HEAD
# Working directory is now clean
# Go back to match remote exactly
git reset --hard origin/main
# Local is now identical to remote📊 Reset Comparison Table
| Mode | HEAD | Index | Working Dir | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
--soft | ✅ Moves | ❌ Unchanged | ❌ Unchanged | Squash commits |
--mixed | ✅ Moves | ✅ Resets | ❌ Unchanged | Reorganize commits |
--hard | ✅ Moves | ✅ Resets | ✅ Resets | Delete everything |
Visual Memory Aid
Repository Index Working Dir
--soft ↩️ - -
--mixed ↩️ ↩️ -
--hard ↩️ ↩️ ↩️
↩️ = reset/moved back
- = unchanged🛟 Emergency Recovery: The Reflog
Even after a hard reset, Git keeps a reflog - a history of where HEAD has been!
# See recent HEAD history
git reflog
# abc1234 HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to HEAD~3
# def5678 HEAD@{1}: commit: important work
# ghi9012 HEAD@{2}: commit: more work
# Recover the "lost" commit!
git reset --hard def5678
# or
git reset --hard HEAD@{1}🎯 Key Takeaways
Keep changes staged, perfect for squashing
Unstage changes, perfect for reorganizing
Destroy everything, use with caution!
Your safety net for recovery
🧠 Quiz: Test Your Understanding
1. What does `git reset --soft HEAD~3` do?
It moves HEAD back 3 commits, but keeps all changes from those 3 commits staged in the index. Perfect for squashing 3 commits into 1!
2. Which reset mode can cause data loss?
--hard! It resets the working directory, destroying any uncommitted changes. The other modes preserve your working directory.
3. How do you recover after an accidental `git reset --hard`?
Use git reflog to find the commit SHA before the reset, then git reset --hard <sha> to restore it. But act fast - reflog entries expire!
4. What's the difference between `HEAD~2` and `HEAD^2`?
HEAD~2= 2 commits back (grandparent)HEAD^2= Second parent of HEAD (only meaningful for merge commits)
🚀 What's Next?
📜 Next: Advanced History Rewriting
Learn about interactive rebase, cherry-pick, and fixing pushed commits!