Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Azure 🔐
Why RBAC Exists (The Problem It Solves)
Imagine managing permissions the old way:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 10,000 users × 1,000 resources = MILLIONS of permissions │
│ │
│ Student1 → Read → StorageAccount1 │
│ Student1 → Write → StorageAccount1 │
│ Student1 → Read → VM1 │
│ ... and on and on forever 😵 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘What goes wrong:
- 👴 Long-time employees accumulate permissions like Pokemon cards
- 👶 New employees wait months to get the right access
- 🎫 Help desk drowns in "I need access to X" tickets
- 🔓 Security holes everywhere
How RBAC Fixes This
Instead of assigning 250 permissions to a developer, you just say:
"You're a Developer" → Boom, they get all developer permissions
Benefits:
- New employee? Assign them the
Developerrole. Done. - Someone leaves? Remove the role. All permissions gone.
- Need to change what developers can do? Update the role once, affects everyone.
The Three Permission Levels (Memorize This!)
| Role | Can Do | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Reader | View only | Auditors, Reporting |
| Contributor | Read + Write + Delete | Developers, Operators |
| Owner | Everything + Assign roles to others | Admins |
💡 Key difference: Contributor can do everything Owner can... EXCEPT assign roles to others.
Two Types of Roles in Azure
This trips people up on the exam! There are TWO separate role systems:
| Entra ID Roles | Azure RBAC Roles |
|---|---|
| Manage the directory itself | Manage Azure resources |
| ~90 built-in roles | Hundreds of built-in roles |
| Found in: Entra ID → Roles | Found in: Resource → Access Control (IAM) |
Scope: Where Permissions Apply
Permissions cascade DOWN, not up:
| Scope Level | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription | Owner on subscription | Owner of EVERYTHING in it |
| Resource Group | Contributor on RG-Dev | Can modify anything in that RG |
| Resource | Reader on StorageAccount1 | Can only read that one storage account |
| Child | Reader on Container1 | Can only read that specific container |
⚠️ Exam Tip: If you assign a role at subscription level, it inherits to ALL resource groups and resources below.
🔬 Lab: Switch Storage Account from Keys to RBAC
By default, storage accounts use Access Keys (anyone with the key = full access).
Let's switch to RBAC for proper security:
Step 1: Create Storage Account
Create a basic storage account (any region, standard settings).
Step 2: Disable Access Keys, Enable Entra ID
Go to Storage Account → Configuration:
☑️ Enable Azure Active Directory authorization
☐ Allow storage account key access ← DISABLE THIS⚠️ Warning: This immediately breaks ALL existing key-based access. Don't do this on production without planning!
Step 3: The Surprise - You Still Can't Access Data!
Even as Owner of the storage account, you can't read/write blobs!
Why? Because:
- Resource permissions ≠ Data permissions
- Owner lets you manage the resource (settings, delete it, etc.)
- But accessing the DATA inside requires separate data roles
Step 4: Assign Data Permissions
Go to Storage Account → Access Control (IAM) → Add role assignment:
| Role | What it gives you |
|---|---|
| Storage Blob Data Reader | Read containers and blobs |
| Storage Blob Data Contributor | Read + Write + Delete |
| Storage Blob Data Owner | Everything + manage permissions |
Assign Storage Blob Data Owner to yourself.
Now you can upload, download, delete blobs! 🎉
🔬 Lab: Creating Custom Roles
What if built-in roles aren't quite right?
Scenario: You want a "Contributor who can't delete" role.
Step 1: Go to Subscription → Access Control → Create Custom Role
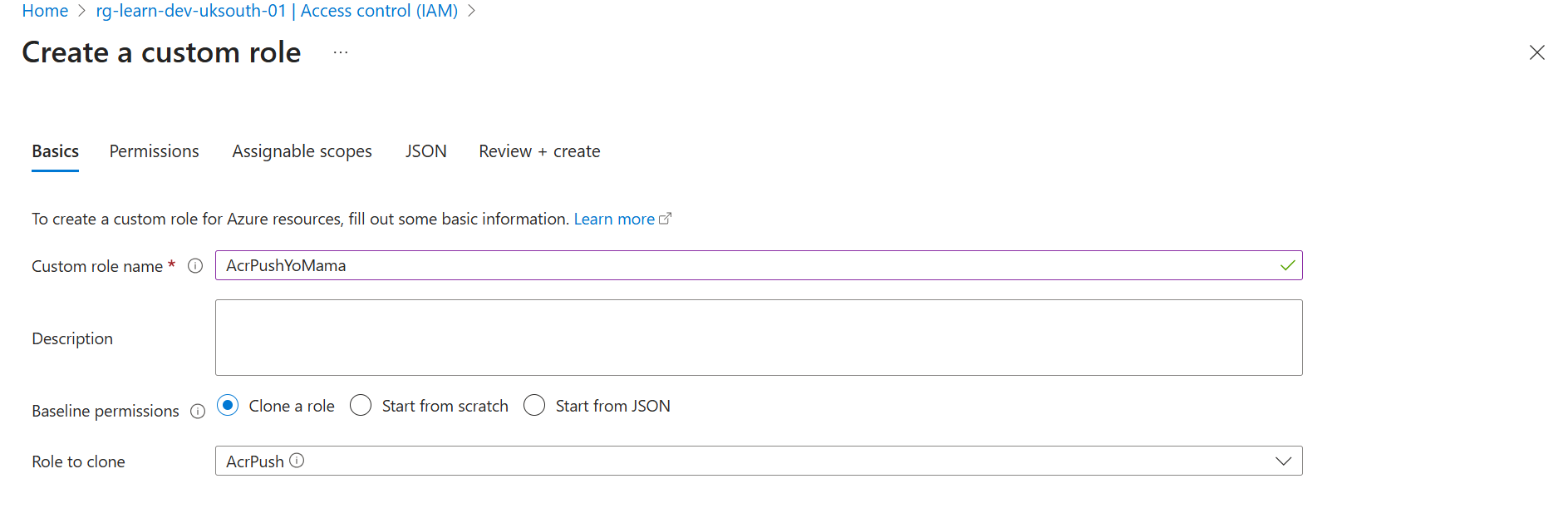
Step 2: Clone an Existing Role
Start from Storage Blob Data Contributor and modify it:
{
"Name": "Storage Blob Data Contributor Without Delete",
"Actions": [
"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/read",
"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/write"
// ❌ Removed: .../containers/delete
],
"DataActions": [
"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read",
"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/write"
// ❌ Removed: .../blobs/delete
]
}Step 3: Create and Assign
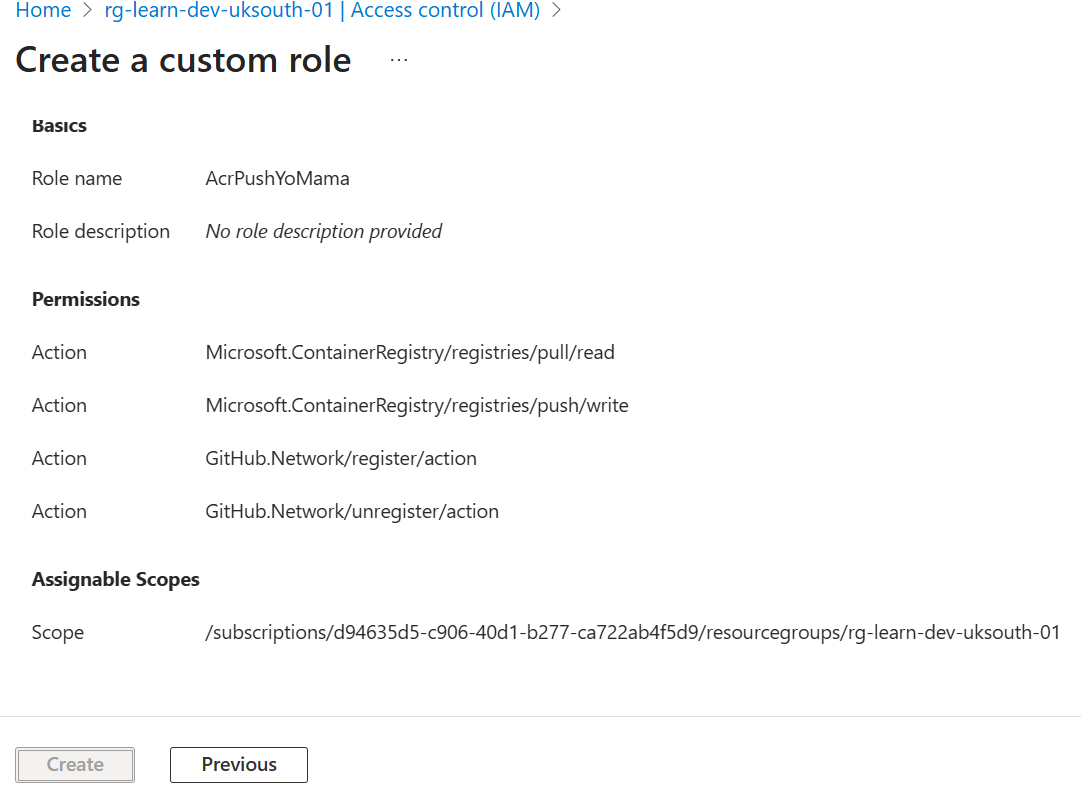
📝 Limit: You can create up to 5,000 custom roles per tenant.
🔬 Lab: Resource Group Scope in Action
Common production pattern:
| Resource Group | Who Gets Access | Role |
|---|---|---|
| RG-Development | All developers | Contributor |
| RG-Production | Only senior devs + ops | Reader (most), Contributor (few) |
Assign Contributor to Dev RG:
Resource Group: RG-Development
Role: Contributor
Members: Student1, Student2, Student3Assign Reader to Prod RG:
Resource Group: RG-Production
Role: Reader
Members: Student1, Student2, Student3Result: Students can break stuff in dev (and learn), but can only look at production.
⚠️ Permissions Merge, Never Subtract: If someone has Contributor from one assignment and Reader from another, they get Contributor (the higher one). You can't "take away" with another assignment.
Interpreting Access Assignments
Two ways to check "who has access to what":
Method 1: Resource-Centric View
Go to: Resource → Access Control (IAM) → Role Assignments
Shows everyone who can access THIS resource.
Method 2: User-Centric View
Go to: Entra ID → Users → Pick User → Azure Role Assignments
Shows everything THIS user can access.
| View | Use When |
|---|---|
| Resource-centric | "Who can access my production database?" |
| User-centric | "What can this employee access?" (offboarding) |
Quick Reference for AZ-104 📋
Built-in Role Hierarchy
Owner > Contributor > Reader
│
└── Only Owner can assign roles to othersData vs Resource Permissions
Storage Account Owner ≠ Can read blobs
You need "Storage Blob Data *" roles for data accessScope Inheritance
Management Group → Subscription → Resource Group → Resource
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Inherited Inherited Inherited DirectKey Portal Locations
| Task | Where |
|---|---|
| Entra admin roles | Entra ID → Roles and administrators |
| Resource RBAC | Any resource → Access Control (IAM) |
| Custom roles | Subscription → Access Control → Create custom role |
| Check user access | Entra ID → Users → [User] → Azure role assignments |
Exam Gotchas 🎯
- Contributor can't assign roles - only Owner can
- Data permissions are separate - Resource Owner ≠ Data Owner
- Permissions merge - you can't subtract, only add
- Deny assignments exist but only through Azure Blueprints, not portal
- Custom roles need P1/P2 for Entra roles (Azure RBAC custom roles work on any tier)
Principle of Least Privilege ⚖️
The golden rule Microsoft loves to test:
Give users the minimum permissions needed to do their job. Nothing more.
Bad: Everyone is Global Admin (convenient but dangerous)
Good:
- Developers → Contributor on Dev RG only
- Ops → Contributor on Prod, Reader on Dev
- Auditors → Reader everywhere
- Admins → Owner (sparingly)
Next up: Privileged Identity Management (PIM) - Just-in-time admin access 🚀