Entra ID Access Control for Azure Storage
Lecture 12: Entra ID Access ControlScott Duffy AZ-104Overview
Up to this point, all storage access has relied on access keys -- a claims-based model where possessing the secret grants full access. Entra ID access control flips the paradigm from "what you have" (key/token) to "who you are" (identity). Once authenticated with Azure via Microsoft Entra ID, a user is granted permissions through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which may or may not include access to a particular storage account, container, or file share.
This is identity-based access instead of secret-based access. For General Purpose v2 storage accounts, Entra ID authorization is available by default -- no additional enablement is needed.
Identity-Based vs. Claims-Based Authentication
Claims-based (access keys/SAS): If you possess the secret, you have access. There is no identity trail, and revocation means rotating or invalidating the secret itself.
Identity-based (Entra ID/RBAC): You authenticate as a known identity. Azure evaluates what roles have been assigned to that identity and grants access accordingly. Every action is tied to a specific user or service principal with a full audit trail.
Critical Exam Concept -- Control Plane vs. Data Plane
Even if you have the Owner role on a storage account (control plane), you cannot read blob data without a separate data plane role such as Storage Blob Data Reader or Storage Blob Data Contributor. The Owner role controls management operations (scaling, configuration, access policies), not data operations. This distinction is heavily tested on the AZ-104 exam.
Access Methods Comparison
| Aspect | Storage Account Keys | Entra ID (RBAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Claims-based ("what you have") | Identity-based ("who you are") |
| Authentication | Present the key | Authenticate with Azure Entra ID |
| Granularity | Full account access | Per-resource, per-container, per-role |
| Audit trail | No user identification | Full user/identity tracking |
| Revocation | Rotate key (affects all consumers) | Remove role assignment (per-user) |
| Legacy support | Supported by all applications historically | Requires Entra-aware applications |
| Security risk | High if key is compromised | Lower -- no shared secrets |
| Default state | Enabled | Available (roles must be assigned) |
Authentication Evolution
Enabling Entra ID and Disabling Key Access
Entra ID authorization is available by default on General Purpose v2 accounts. The key decision is whether to disable storage account key access to force all authentication through Entra ID.
Disabling Key Access in the Portal
- Navigate to the storage account overview
- Under Security, observe "Storage account key access: Enabled"
- Click to navigate to Settings > Configuration
- Set Allow storage account key access to Disabled
- Click Save
Disabling Key Access -- Immediate Impact
Once storage account key access is disabled, ALL of the following immediately become invalid:
- Both storage account keys (key1 and key2)
- All SAS tokens (service, account, and user delegation SAS generated from account keys)
- All stored access policies relying on account keys
Only Entra ID authentication and user delegation SAS (signed with Entra credentials) will continue to work. Ensure all consumers are migrated to Entra ID before disabling key access.
Access Control Levels
Entra ID roles can be assigned at two distinct levels for blob storage, providing different scopes of access.
RBAC Scope Hierarchy
direction: down
title: RBAC Scope Hierarchy {
style.font-size: 28
}
account: Storage Account {
style.fill: "#e8f4f8"
style.stroke: "#38a"
note: "Account-level roles apply to ALL containers" {
style.fill: "#d4e8f4"
style.font-size: 14
}
container1: Container 1 {
style.fill: "#f4e8f4"
style.stroke: "#a63"
note: "Container-level roles apply to THIS container only" {
style.fill: "#e8d4e8"
style.font-size: 14
}
blobA: Blob A {style.fill: "#e8e8e8"}
blobB: Blob B {style.fill: "#e8e8e8"}
}
container2: Container 2 {
style.fill: "#f4e8f4"
style.stroke: "#a63"
note: "Container-level roles apply to THIS container only" {
style.fill: "#e8d4e8"
style.font-size: 14
}
blobC: Blob C {style.fill: "#e8e8e8"}
blobD: Blob D {style.fill: "#e8e8e8"}
}
}Account Level
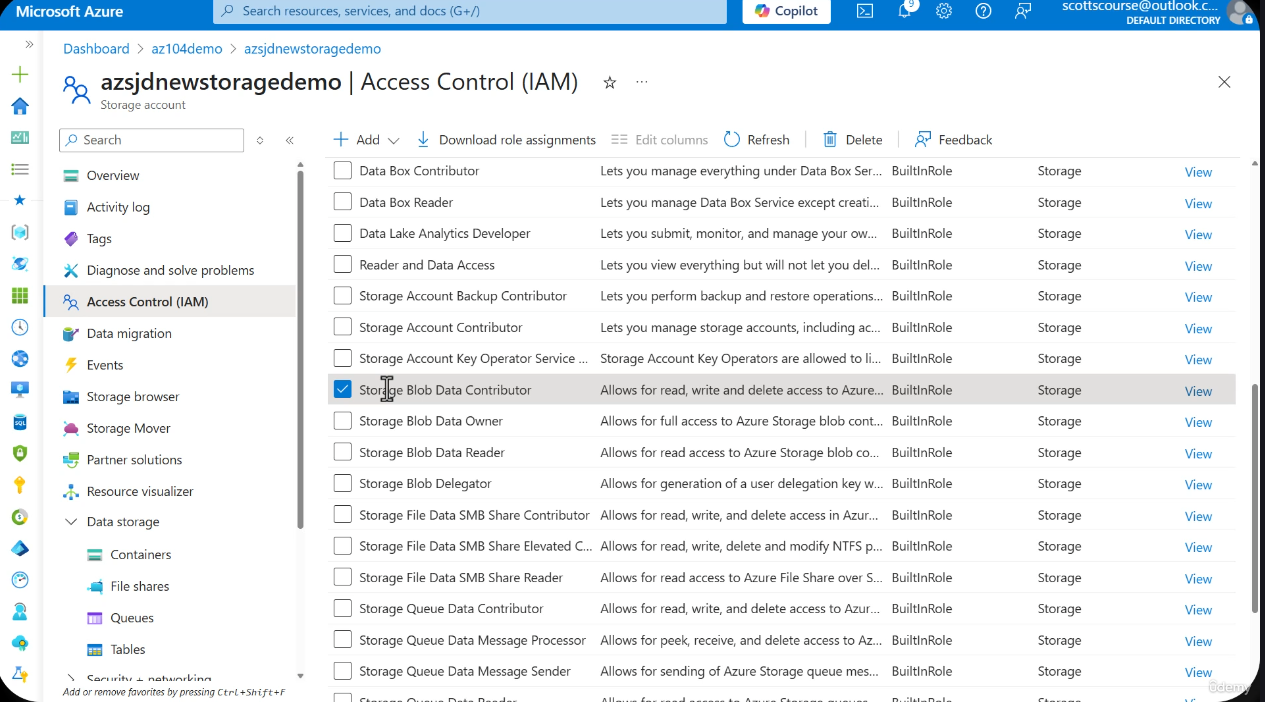
Access Control is available directly from the storage account overview screen. Assigning a role here applies to all containers within the storage account.
- Navigate to the storage account overview
- Click Access Control (IAM) in the left menu
- Click Add > Add role assignment
- Search for storage-related roles (e.g., "Storage Blob Data Contributor")
- Select the role, choose the user/group/service principal
- Click Review + assign
Account-Level Role Example
Assigning Storage Blob Data Contributor at the account level grants read, write, and delete access to blobs across all containers in the storage account. This is convenient but less secure than container-level assignment.
Container Level
For more granular control, roles can be assigned at the individual container level.
- Navigate to the specific container
- Click Access Control (IAM) in the container properties
- Click Add > Add role assignment
- Select the desired role and assignee
- Click Review + assign
Container-Level Scoping is More Secure
Assigning roles at the container level limits the blast radius. A user with Storage Blob Data Contributor on a single container can only read, write, and delete blobs in that specific container -- not in any other containers within the same storage account.
Key RBAC Roles for Storage
Complete Storage RBAC Role Reference
| Role | Plane | Permissions | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Blob Data Owner | Data | Full CRUD + set POSIX ACLs on blobs/containers | Admin / full blob management |
| Storage Blob Data Contributor | Data | Read, write, delete blobs and containers | Developers / application access |
| Storage Blob Data Reader | Data | Read-only access to blobs | Reporting, auditing, read-only consumers |
| Storage Blob Delegator | Data | Generate user delegation keys | SAS generation via Entra identity |
| Storage Account Contributor | Control | Manage account settings, configuration, keys | Ops / infrastructure management |
| Storage Account Key Operator Service Role | Control | List and regenerate storage account keys | Key rotation automation |
| Reader and Data Access | Both | Read all data + list storage account keys | Read-only administrative access |
| Storage File Data SMB Share Contributor | Data | SMB read, write, delete on file shares | File share users |
| Storage File Data SMB Share Elevated Contributor | Data | SMB read, write, delete + modify NTFS ACLs | File share admins |
| Storage File Data SMB Share Reader | Data | SMB read-only access to file shares | File share read-only users |
| Storage File Data Privileged Contributor | Data | Full file data read, write, delete, modify ACLs | Privileged file operations |
Exam Pitfall -- Storage Account Contributor vs. Data Roles
Storage Account Contributor is a control plane role. It allows managing the storage account itself (configuration, networking, keys) but does not grant access to read, write, or delete blob data. You need a data plane role like Storage Blob Data Contributor for data access. This is a frequently tested distinction.
Control Plane vs. Data Plane Explained
- Control plane roles: Manage the resource itself (create/delete accounts, configure settings, manage keys). These roles operate through Azure Resource Manager (ARM).
- Data plane roles: Access the data stored within the resource (read/write/delete blobs, files, tables, queues). These roles operate directly against the storage service endpoints.
A user can have full control plane access (Owner/Contributor) and still be unable to read a single blob without a data plane role assignment.
Portal Access with Entra ID
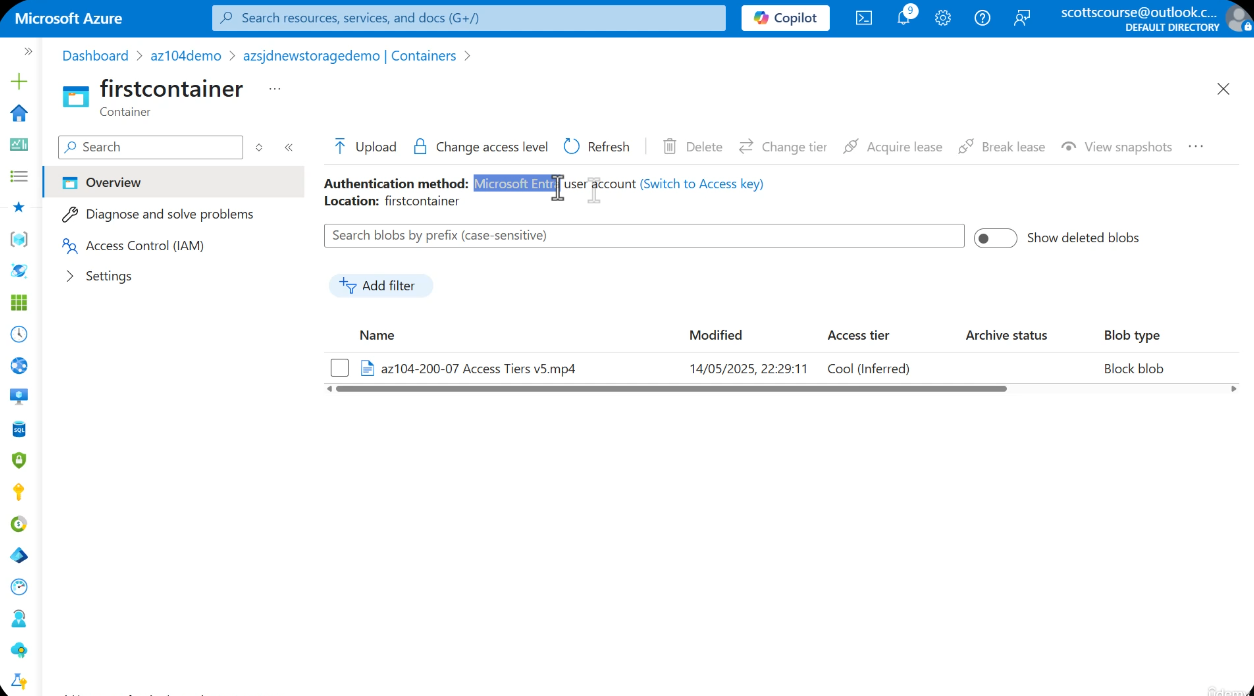
When key access is disabled and Entra ID is the default authentication method, the portal experience changes.
Behavior Without Proper Roles
If you navigate to a container in the portal without an appropriate Entra ID data role, you will see a message:
"You do not have permissions to list the data using your user account with Microsoft Entra ID."
This occurs even if you are the account owner or have the Owner role on the storage account, because the Owner role is a control plane role and does not grant data access.
Self-Assignment Workflow
- Navigate to the container's Access Control (IAM)
- Click Add > Add role assignment
- Select Storage Blob Data Contributor
- Under Members, select your own account
- Click Review + assign twice to confirm
- Under View my access, confirm the role appears (e.g., "Administrator at Management Group + Blob Data Contributor for this resource")
Propagation Delay
Role assignments take a few seconds to propagate. If access is not immediately available after assignment, wait 10-30 seconds and refresh the portal page. The authentication method displayed in the portal will show Microsoft Entra ID.
Configuration Workflow
When to Use What -- Decision Flowchart
Advantages Over Keys
Why Entra ID is the Recommended Approach
- No hardcoded secrets -- Applications authenticate via identity, not embedded keys
- Fine-grained role-based control -- Assign specific permissions to specific users/groups per resource
- User identification and audit trail -- Every action is attributable to a specific identity
- Easier permission revocation -- Remove a role assignment without affecting other users
- Enterprise identity management -- Integrates with existing Entra ID policies (MFA, conditional access, PIM)
- No key rotation burden -- No shared secrets to rotate across all consumers
Disadvantages
Trade-offs to Consider
- More complex initial setup -- Requires understanding of RBAC roles and assignments
- Applications must be Entra-aware -- Legacy applications may not support Entra authentication
- Slight additional latency -- Role evaluation adds minimal overhead to each request
- Requires proper RBAC policy understanding -- Misconfigured roles can lead to over- or under-permissioning
- Propagation delay -- Role assignments are not instantaneous
Added Value -- Beyond the Lecture
Managed Identity Access Pattern
Managed Identity -- VM to Storage Without Any Keys
A common pattern for Azure VMs or App Services accessing storage without any keys or secrets:
- Enable a system-assigned managed identity on the VM/App Service
- Assign a storage data role (e.g., Storage Blob Data Contributor) to the managed identity
- The application on the VM uses the Azure SDK to obtain a token from the Instance Metadata Service (IMDS)
- The token is used to authenticate against the storage account -- no keys, no secrets, no credentials in code
This is the gold standard for service-to-service authentication in Azure -- zero secrets in code, automatic token rotation, and full RBAC control.
ABAC -- Attribute-Based Access Control
ABAC Conditions for Fine-Grained Blob Access
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) extends RBAC by adding conditions based on resource attributes. For example, you can grant a user Storage Blob Data Reader access, but only for blobs that have a specific blob index tag.
Example condition: User can read blobs only where project=finance tag is set.
This enables scenarios where a single container holds data for multiple projects, and each team can only access blobs tagged for their project -- without splitting data across multiple containers.
ABAC conditions are configured as part of the role assignment and evaluated at runtime alongside the RBAC check.
Default Behavior Reminder
Even with Owner Role, You Cannot Read Blobs
By default, even the Owner role on a storage account does not grant blob data access. The Owner role is a control plane role -- it can manage the account but not read, write, or delete data. You must explicitly assign a data plane role (Storage Blob Data Reader, Contributor, or Owner) to access blob data. This catches many administrators by surprise and is a frequent exam question.
CLI and PowerShell Reference
Disable / Re-enable Storage Account Key Access
# Disable storage account key access (force Entra ID only)
az storage account update \
--name myaccount \
--resource-group myRG \
--allow-shared-key-access false
# Re-enable key access
az storage account update \
--name myaccount \
--resource-group myRG \
--allow-shared-key-access true# Disable storage account key access (force Entra ID only)
Set-AzStorageAccount `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-Name "myaccount" `
-AllowSharedKeyAccess $false
# Re-enable key access
Set-AzStorageAccount `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-Name "myaccount" `
-AllowSharedKeyAccess $trueAssign Roles at Account Level
# Assign Storage Blob Data Contributor at account level
az role assignment create \
--assignee user@contoso.com \
--role "Storage Blob Data Contributor" \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}# Assign Storage Blob Data Contributor at account level
New-AzRoleAssignment `
-SignInName "user@contoso.com" `
-RoleDefinitionName "Storage Blob Data Contributor" `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}"Assign Roles at Container Level
# Assign Storage Blob Data Reader at container level
az role assignment create \
--assignee user@contoso.com \
--role "Storage Blob Data Reader" \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}/blobServices/default/containers/{container}# Assign Storage Blob Data Reader at container level
New-AzRoleAssignment `
-SignInName "user@contoso.com" `
-RoleDefinitionName "Storage Blob Data Reader" `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}/blobServices/default/containers/{container}"Check Current Role Assignments
# List role assignments at account level
az role assignment list \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account} \
--output table
# List role assignments for a specific user
az role assignment list \
--assignee user@contoso.com \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account} \
--output table# List role assignments at account level
Get-AzRoleAssignment `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}" | `
Format-Table DisplayName, RoleDefinitionName, Scope
# List role assignments for a specific user
Get-AzRoleAssignment `
-SignInName "user@contoso.com" `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}" | `
Format-Table RoleDefinitionName, ScopeManaged Identity Role Assignment
# Enable system-assigned managed identity on a VM
az vm identity assign \
--name myVM \
--resource-group myRG
# Get the VM's managed identity principal ID
PRINCIPAL_ID=$(az vm show \
--name myVM \
--resource-group myRG \
--query "identity.principalId" \
--output tsv)
# Assign Storage Blob Data Contributor to the managed identity
az role assignment create \
--assignee "$PRINCIPAL_ID" \
--role "Storage Blob Data Contributor" \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}# Enable system-assigned managed identity on a VM
$vm = Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "myRG" -Name "myVM"
Update-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "myRG" -VM $vm -IdentityType SystemAssigned
# Get the VM's managed identity principal ID
$principalId = (Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "myRG" -Name "myVM").Identity.PrincipalId
# Assign Storage Blob Data Contributor to the managed identity
New-AzRoleAssignment `
-ObjectId $principalId `
-RoleDefinitionName "Storage Blob Data Contributor" `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}"MS Learn References
- Authorize access to blobs using Microsoft Entra ID
- Authorize access to data in Azure Storage
- Azure built-in roles for Storage
- Authorize access to blobs using Azure ABAC conditions
- Lab 07 -- Manage Azure Storage
Lab Exercises
Prerequisites
Ensure you have an active Azure subscription (a free trial works), the Azure CLI installed locally or access to Azure Cloud Shell, and a storage account with at least one blob container already created.
Lab 1: Assign Yourself Storage Blob Data Contributor at Account Level
- Navigate to your storage account in the Azure Portal
- Click Access Control (IAM) in the left menu
- Click Add > Add role assignment
- Search for and select Storage Blob Data Contributor
- Click Next, then under Members select your own account
- Click Review + assign twice to confirm
- Click View my access and verify the role appears
Lab 2: Browse Storage via Storage Browser with Entra ID
- In the storage account, navigate to Storage Browser in the left menu
- Open a blob container and verify you can list and view blobs
- Observe the authentication method displayed -- it should show Microsoft Entra ID
- Upload a test file and download it to confirm read/write access
Lab 3: Disable Storage Account Key Access
- Navigate to Settings > Configuration in the storage account
- Set Allow storage account key access to Disabled
- Click Save
- Navigate to Security + networking > Access keys -- observe the keys are no longer usable
- Attempt to generate a new SAS token -- observe that key-based SAS generation fails
Lab 4: Verify Keys and SAS Tokens Stop Working
- Copy a previously generated SAS URL (from earlier labs)
- Attempt to access the blob using the SAS URL in a browser or via
curl - Observe the 403 Forbidden or AuthenticationFailed error
- Confirm that Entra ID authenticated access (Storage Browser) still works
Lab 5: Assign a Different User Storage Blob Data Reader at Container Level
- Navigate to a specific container's Access Control (IAM)
- Click Add > Add role assignment
- Select Storage Blob Data Reader
- Choose a different user or service principal as the member
- Click Review + assign
- Have the other user verify they can read (but not write or delete) blobs in that specific container
- Have them verify they cannot access blobs in other containers
Lab 6: Re-enable Key Access
- Navigate to Settings > Configuration
- Set Allow storage account key access to Enabled
- Click Save
- Verify that access keys are available again under Security + networking > Access keys
Lab 7: Complete the Official Microsoft Lab
Complete the full official lab exercise: Lab 07 -- Manage Azure Storage
Clean Up
After completing the labs, remove any role assignments you no longer need and consider re-enabling key access if other applications depend on it:
# Remove a role assignment
az role assignment delete \
--assignee user@contoso.com \
--role "Storage Blob Data Contributor" \
--scope /subscriptions/{sub-id}/resourceGroups/{rg}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{account}
# Re-enable key access if needed
az storage account update --name myaccount --resource-group myRG --allow-shared-key-access true