Azure Storage Data Protection
AZ-104 Scott Duffy - Lecture 6 StorageOverview
Azure Storage provides multiple layers of data protection to guard against accidental deletion, malicious tampering, and data corruption. These features work together as layered defenses: point-in-time restore, soft delete, versioning, change feed, and immutability. Understanding how they interrelate and their dependency chain is critical for the AZ-104 exam and real-world storage administration.
Point-in-Time Restore
Point-in-time restore allows you to restore an entire container (or a subset of blobs) to a specific previous state within a defined restoration window.
Key Facts
- Maximum restoration window: 30 days
- Can restore an entire container to a specified date and time
- Example scenario: Restore to the state from 21 days ago to recover from bulk accidental changes
Prerequisites -- All Three Required
Point-in-time restore requires all of the following to be enabled simultaneously:
- Versioning -- must be on
- Change feed -- must be on
- Blob soft delete -- must be on
If any one of these is disabled, point-in-time restore cannot function.
direction: right
pitr: Point-in-Time Restore {
style.fill: "#2ecc71"
style.font-color: "#fff"
style.stroke: "#27ae60"
}
versioning: Versioning {
style.fill: "#f39c12"
style.font-color: "#fff"
style.stroke: "#e67e22"
}
change_feed: Change Feed {
style.fill: "#9b59b6"
style.font-color: "#fff"
style.stroke: "#8e44ad"
}
soft_delete: Blob Soft Delete {
style.fill: "#3498db"
style.font-color: "#fff"
style.stroke: "#2980b9"
}
pitr -> versioning: requires {
style.stroke: "#e74c3c"
style.font-color: "#e74c3c"
}
pitr -> change_feed: requires {
style.stroke: "#e74c3c"
style.font-color: "#e74c3c"
}
pitr -> soft_delete: requires {
style.stroke: "#e74c3c"
style.font-color: "#e74c3c"
}How It Works
When point-in-time restore is triggered, Azure uses the change feed log to replay blob state back to the target timestamp. The versioning system provides the actual blob data at each point, and soft delete ensures that deleted blobs are still recoverable within the window.
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Max restore window | 30 days |
| Granularity | Container or blob prefix |
| Required features | Versioning + Change Feed + Soft Delete |
| Storage account type | General-purpose v2 |
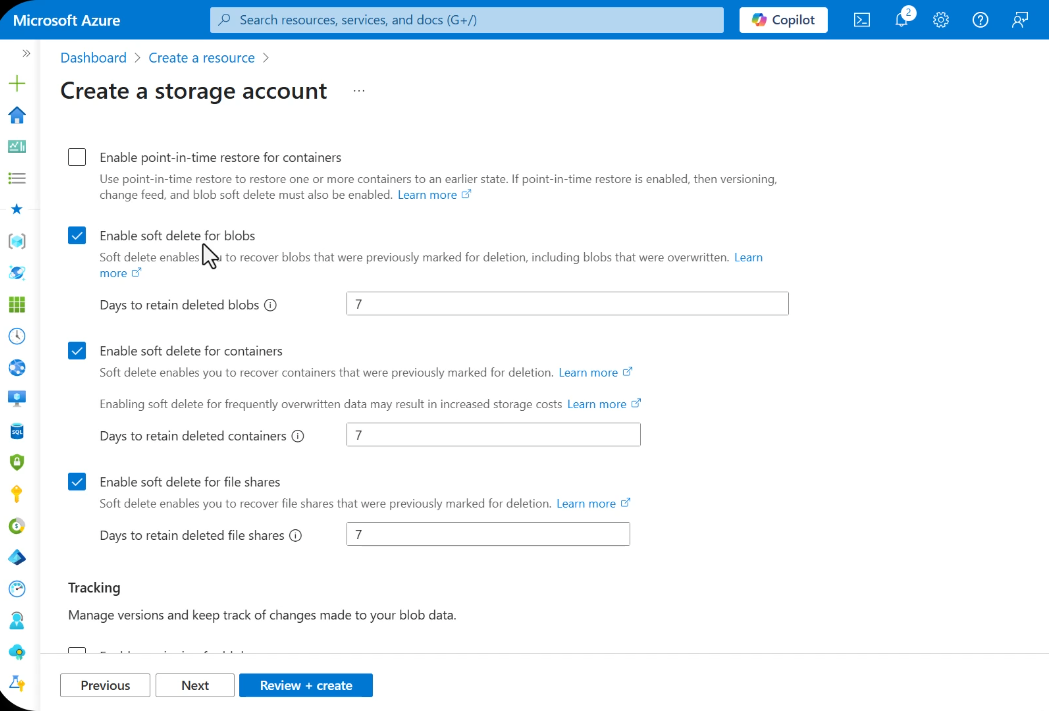
Soft Delete
Soft delete is a safety net that marks blobs, containers, or file shares as deleted rather than permanently removing them. This provides a configurable grace period during which deleted data can be recovered.
Default Behavior
- Enabled by default on new storage accounts
- Default retention: 7 days (configurable up to 365 days)
- Deleted items are retained in a soft-deleted state and do not appear in normal listings
Three Variants of Soft Delete
| Variant | Scope | What It Protects |
|---|---|---|
| Blob soft delete | Individual blobs and snapshots | Recover accidentally deleted and overwritten blobs |
| Container soft delete | Entire containers | Recover deleted containers and all their contents |
| File share soft delete | Azure file shares | Recover deleted file shares |
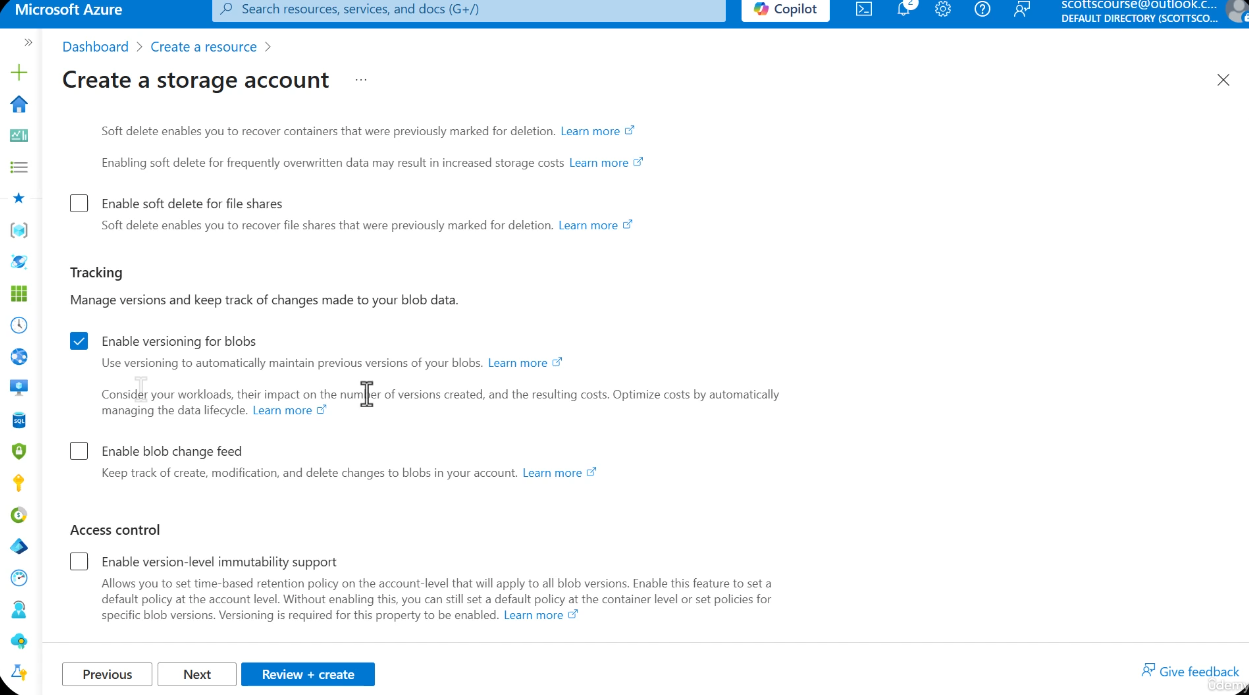
Soft Delete Protects Against Overwrites (Not Just Deletes)
This Is NOT the Same as Versioning
Blob soft delete protects against both deletion and overwrites. When a blob is overwritten, the previous version is saved as a soft-deleted snapshot that can be recovered within the retention window. This is a distinct mechanism from versioning:
- Soft delete on overwrite: The previous blob state is saved as a soft-deleted snapshot with a retention period. It is automatically purged after the retention window expires.
- Versioning on overwrite: The previous blob state is saved as a permanent version that persists until explicitly deleted or removed by lifecycle policy.
Both protect against accidental overwrites, but they work differently:
| Aspect | Soft Delete (Overwrite) | Versioning |
|---|---|---|
| What gets saved | Soft-deleted snapshot | Permanent version |
| Retention | Time-limited (7-365 days) | Indefinite until deleted |
| Auto-cleanup | Yes, after retention expires | No, must use lifecycle rules |
| Cost impact | Temporary (storage during retention) | Ongoing (all versions persist) |
| Recovery method | Undelete / list soft-deleted snapshots | Access by version ID |
From Microsoft Learn -- Soft delete for blobs:
"When blob soft delete is enabled for a storage account, you can recover blobs, blob versions, and snapshots after they are deleted, within a retention period that you specify. Blob soft delete also preserves the overwritten state of a blob by maintaining a soft-deleted snapshot of the blob's previous state."
Impact on Testing and Development
Soft delete can complicate testing workflows. When you delete test files, they are not actually removed -- they persist in a soft-deleted state. To truly remove them you must either:
- Wait for the retention period to expire
- Purge the soft-deleted items manually
This is a common gotcha when scripting cleanup of test environments.
Recovery Process
When a blob is soft-deleted (via deletion or overwrite), it can be recovered by calling the Undelete Blob operation. For overwrites, the previous state is saved as a soft-deleted snapshot that can be listed and restored. The blob returns to its active state with all its properties and metadata intact.
Versioning
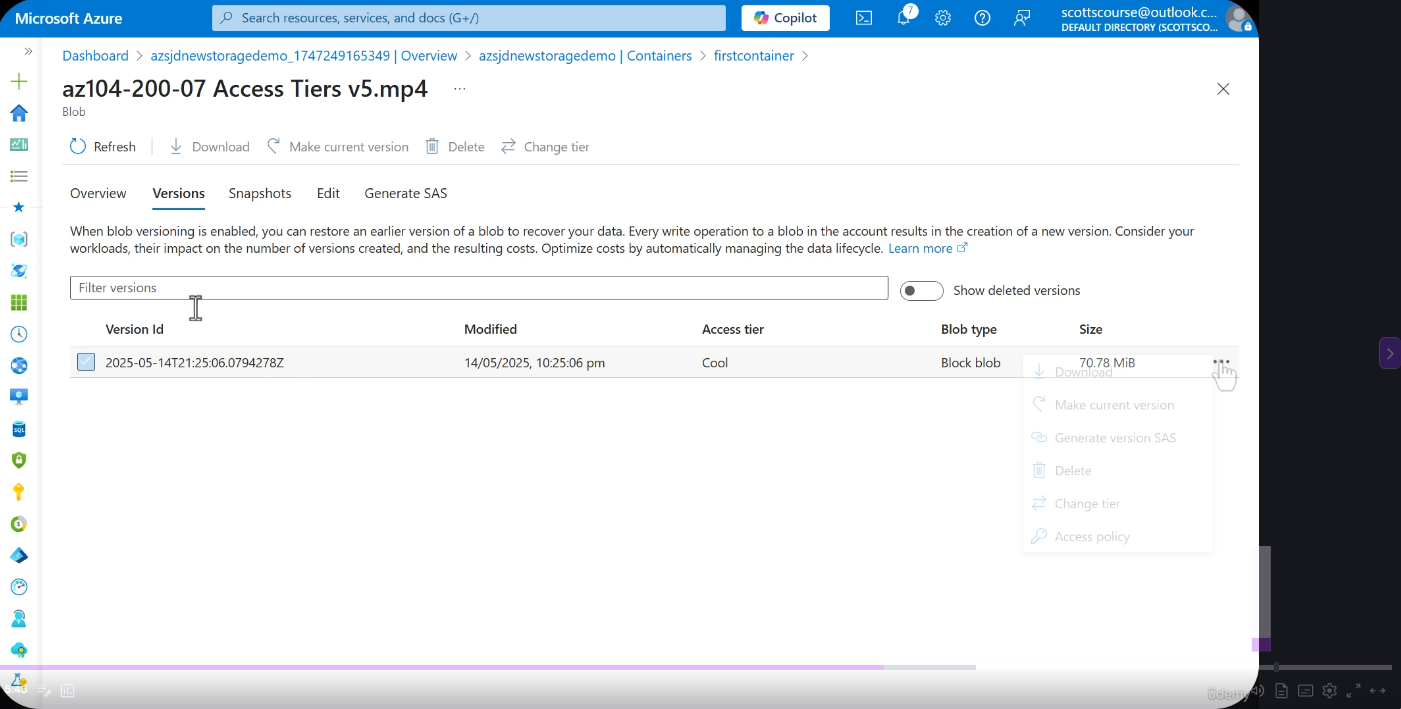
Versioning automatically maintains previous versions of blobs every time they are modified or overwritten. Each version is an immutable snapshot of the blob at the time of the write operation.
How It Works
- Every modification creates a new version automatically
- Example: A file updated every 30 days will accumulate versions (v6, v7, v8, etc.)
- Previous versions are read-only and immutable
- Useful for audit trails and accidental modification recovery
Version Browsing in Practice
Cost Implications -- Critical for Exam and Production
You pay for each version stored. Storage costs multiply based on update frequency:
- A blob updated daily with versioning enabled will store 30 versions per month
- Depending on update frequency, versioning can increase storage costs by 2x to 10x
- Use lifecycle management policies to move old versions to cooler tiers (Cool, Cold, Archive) or delete them after a retention period
Lifecycle Management for Versions
You can configure lifecycle management rules to automatically transition or delete old versions:
| Action | Example Rule |
|---|---|
| Move to Cool tier | Versions older than 30 days |
| Move to Archive tier | Versions older than 90 days |
| Delete old versions | Versions older than 365 days |
Change Feed
The change feed provides a transaction log of all create, modify, and delete operations on blobs in a storage account. It is stored in the $blobchangefeed container.
Change Feed Details
- Logs all create, modify, and delete operations on blobs
- Format: Apache Avro (compact binary format)
- Can be consumed by listening to the feed or querying it
- Enables event-driven actions based on changes
- Use cases: compliance auditing, automation pipelines, alerting
Change Feed vs Event Grid
| Feature | Change Feed | Event Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery model | Pull (poll/query) | Push (event subscription) |
| Data format | Apache Avro | JSON (CloudEvents) |
| Retention | Configurable | Transient |
| Ordering | Guaranteed per blob | Best effort |
| Use case | Audit, compliance, replay | Real-time reactions |
Immutability
Immutability ensures that once a blob is written, it cannot be altered or deleted for a specified retention period. This implements WORM (Write Once Read Many) storage.
Immutability Is Irreversible (When Locked)
Once an immutability policy is locked, it cannot be decreased or removed. Blobs under a locked policy cannot be deleted even by the storage account owner or an Azure administrator. Plan retention periods carefully.
Configuration Levels
| Level | Scope | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Account-level | Applies to all containers | Broadest scope |
| Container-level | Applies to all blobs in the container | Most common configuration |
| Version-level | Applies to specific blob versions | Requires versioning enabled |
Policy Types
Time-Based Retention Policy
- Blobs cannot be modified or deleted for a specified number of days
- Policy can be unlocked (modifiable) or locked (immutable itself)
- Once locked, the retention period can only be increased, never decreased
Legal Hold
- Blobs cannot be modified or deleted until the legal hold is explicitly cleared
- No expiration date -- remains until removed
- Multiple legal holds can be applied (identified by tags)
- Use case: Litigation, investigations, regulatory holds
| Feature | Time-Based Retention | Legal Hold |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Fixed period (days) | Indefinite until cleared |
| Can be removed? | Only if unlocked | Yes, by clearing the hold |
| Expiration | Automatic after period | Manual removal only |
| Multiple policies | One per container | Multiple tags supported |
Compliance Standards
Immutable storage meets the requirements for:
- SEC Rule 17a-4(f) -- Securities and Exchange Commission
- FINRA Rule 4511 -- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority
- CFTC Rule 1.31 -- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- WORM compliance (Write Once Read Many)
Use Cases
- Security logs that cannot be tampered with
- Compliance records for financial services
- Audit trails for regulated industries
- Evidence preservation -- prevents malicious deletion
- Healthcare records (HIPAA)
Immutability Requires Versioning
When versioning is enabled alongside immutability, the policy applies to all blob versions. This ensures that even previous versions of a blob are protected from deletion or modification.
Blob Lifecycle State Diagram
CLI and PowerShell Commands
# Enable soft delete for blobs with 14-day retention
az storage blob service-properties delete-policy update \
--account-name myaccount \
--enable true \
--days-retained 14
# Enable versioning
az storage account blob-service-properties update \
--account-name myaccount \
--resource-group myRG \
--enable-versioning true
# Enable change feed
az storage account blob-service-properties update \
--account-name myaccount \
--resource-group myRG \
--enable-change-feed true
# Create a time-based immutability policy (365 days)
az storage container immutability-policy create \
--account-name myaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--period 365
# Lock an immutability policy (IRREVERSIBLE)
az storage container immutability-policy lock \
--account-name myaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--if-match "<ETag>"
# Set a legal hold
az storage container legal-hold set \
--account-name myaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--tags "litigation2026"
# Undelete a soft-deleted blob
az storage blob undelete \
--account-name myaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--name myblob.txt
# List blob versions
az storage blob list \
--account-name myaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--include v \
--output table# Enable soft delete for blobs with 14-day retention
Enable-AzStorageBlobDeleteRetentionPolicy `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-RetentionDays 14
# Enable versioning
Update-AzStorageBlobServiceProperty `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-IsVersioningEnabled $true
# Enable change feed
Update-AzStorageBlobServiceProperty `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-EnableChangeFeed $true
# Create a time-based immutability policy (365 days)
Set-AzStorageContainerImmutabilityPolicy `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-ContainerName "mycontainer" `
-ImmutabilityPeriod 365
# Lock an immutability policy (IRREVERSIBLE)
Lock-AzStorageContainerImmutabilityPolicy `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-ContainerName "mycontainer" `
-Etag "<ETag>"
# Set a legal hold
Add-AzStorageContainerLegalHold `
-ResourceGroupName "myRG" `
-StorageAccountName "myaccount" `
-ContainerName "mycontainer" `
-Tag "litigation2026"
# Undelete a soft-deleted blob
$ctx = New-AzStorageContext -StorageAccountName "myaccount" -StorageAccountKey "<key>"
Get-AzStorageBlob -Context $ctx -Container "mycontainer" -Blob "myblob.txt" -IncludeDeleted |
Restore-AzStorageBlobLab Exercise
Hands-On Lab: Data Protection Features
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription
- A General-purpose v2 storage account
- Azure CLI or PowerShell installed
Step 1 -- Enable Soft Delete with 14-Day Retention
az storage blob service-properties delete-policy update \
--account-name <your-account> \
--enable true \
--days-retained 14Verify in the portal under Storage Account > Data protection.
Step 2 -- Upload, Delete, and Recover a Blob
# Create a test file
echo "Hello, data protection!" > testfile.txt
# Upload the blob
az storage blob upload \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--name testfile.txt \
--file testfile.txt
# Delete the blob
az storage blob delete \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--name testfile.txt
# List soft-deleted blobs
az storage blob list \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--include d \
--output table
# Recover the soft-deleted blob
az storage blob undelete \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--name testfile.txtStep 3 -- Enable Versioning and Browse Versions
# Enable versioning
az storage account blob-service-properties update \
--account-name <your-account> \
--resource-group <your-rg> \
--enable-versioning true
# Upload a file
echo "Version 1 content" > versiontest.txt
az storage blob upload \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--name versiontest.txt \
--file versiontest.txt \
--overwrite
# Modify and re-upload
echo "Version 2 content" > versiontest.txt
az storage blob upload \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--name versiontest.txt \
--file versiontest.txt \
--overwrite
# List all versions
az storage blob list \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name testcontainer \
--include v \
--output tableStep 4 -- Enable Change Feed and Observe Entries
# Enable change feed
az storage account blob-service-properties update \
--account-name <your-account> \
--resource-group <your-rg> \
--enable-change-feed true
# Perform some blob operations (upload, modify, delete)
# Then check the $blobchangefeed container for Avro-format logs
az storage blob list \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name '$blobchangefeed' \
--output tableNote: Change feed entries may take a few minutes to appear.
Step 5 -- Create Immutability Policy and Test Deletion
# Create a time-based immutability policy (1 day for testing)
az storage container immutability-policy create \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name immutablecontainer \
--period 1
# Upload a blob to the immutable container
echo "This cannot be deleted" > immutable.txt
az storage blob upload \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name immutablecontainer \
--name immutable.txt \
--file immutable.txt
# Attempt to delete the blob (THIS SHOULD FAIL)
az storage blob delete \
--account-name <your-account> \
--container-name immutablecontainer \
--name immutable.txtExpected output: The delete operation should fail with an error indicating the blob is protected by an immutability policy.
Cleanup
# Remove the legal hold / unlock policy before deleting resources
# Delete the test storage account or containers when finishedMicrosoft Learn References
| Topic | Link |
|---|---|
| Point-in-Time Restore | Overview |
| Blob Soft Delete | Overview |
| Blob Versioning | Overview |
| Immutable Storage | Overview |
| Change Feed | Overview |
Summary
| Feature | Purpose | Default | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point-in-Time Restore | Restore container to prior state | Disabled | Versioning + Change Feed + Soft Delete |
| Soft Delete | Grace period before permanent removal | Enabled (7 days) | None |
| Versioning | Automatic version history on modification | Disabled | None |
| Change Feed | Transaction log of all blob operations | Disabled | None |
| Immutability | WORM -- prevent modification and deletion | Disabled | Versioning (for version-level) |